Computer-Controlled Cutting

Group Assignment
FabLab Indoamérica
1.1 General Safety Guidelines
- Only trained and authorized personnel may operate the machines.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) must be worn when necessary (e.g., safety glasses for the laser cutter).
- Machines should never be operated without supervision.
- Keep the workspace clean and free of flammable objects.
- Ensure ventilation and smoke extraction systems are active before operating the laser cutter.
1.2 Laser Cutter (Epilog FusionMaker) Safety Rules
1.2.1 Before Operation
- Ensure the material is laser-compatible and does not release toxic fumes.
- Check that the laser optics (mirrors and lenses) are clean.
- Set power, speed, and frequency according to the material specifications.
- Close the machine’s lid properly before starting the cut.
1.2.2 During Operation
- Never leave the machine unattended while running.
- Watch the process through the safety window without opening the lid.
- In case of fire, stop the machine immediately and use the lab fire extinguisher.
1.2.3 After Operation
- Wait for the cut pieces to cool before handling.
- Clean any debris from the cutting area.
- Turn off the machine and disconnect it if not in use for an extended period.
2. Vinyl Cutter (Roland) Safety Rules
2.1 Before Operation
- Ensure the blade is properly adjusted and in good condition.
- Set the correct pressure and speed based on the material.
- Align and secure the vinyl properly in the machine.
2.2 During Operation
- Keep hands away from the cutting head while the machine is running.
- Supervise the process to prevent material misalignment or blade damage.
- Stop the machine immediately if an issue occurs.
2.3 After Operation
- Carefully remove the cut material and clean the workspace.
- Turn off the machine when not in use.
- Store blades and tools properly after use.
2.4 Emergency Procedures
- In case of fire, use the CO₂ extinguisher available in the FabLab.
- Report any incidents or machine malfunctions to the FabLab supervisor.
- Follow first aid protocols and contact lab personnel if an injury occurs.
3.1 General Information
- Brand & Model: Epilog FusionMaker
- Type: CO₂ Laser Cutter
- Functionality: Precision cutting and engraving
- Common Uses: Prototyping, fabrication, artistic engraving, industrial applications
3.2 Technical Specifications
- Laser Type: CO₂ laser.
- Power: 30W, 40W, or 50W options.
- Work Area: Approx. 24” x 12” (609 mm x 305 mm).
- Resolution: Up to 1200 DPI
- Speed & Power Control: Adjustable settings.
3.3 Supported Materials
3.3.1 Cutting Capabilities
- Wood (MDF, plywood, etc.)
- Acrylic
- Leather
- Cardboard
- Fabric
- Some plastics (Non-PVC)
3.3.2 Engraving Capabilities
- Glass
- Ceramic
- Coated metals
3.4 Key Features
- Enclosure: Fully enclosed system with a transparent lid.
- Ventilation System: Integrated air exhaust
- Control Panel: Digital interface
- Air Assist: Reduces flaming and improves precision
- Red Dot Pointer: Previews the cutting area
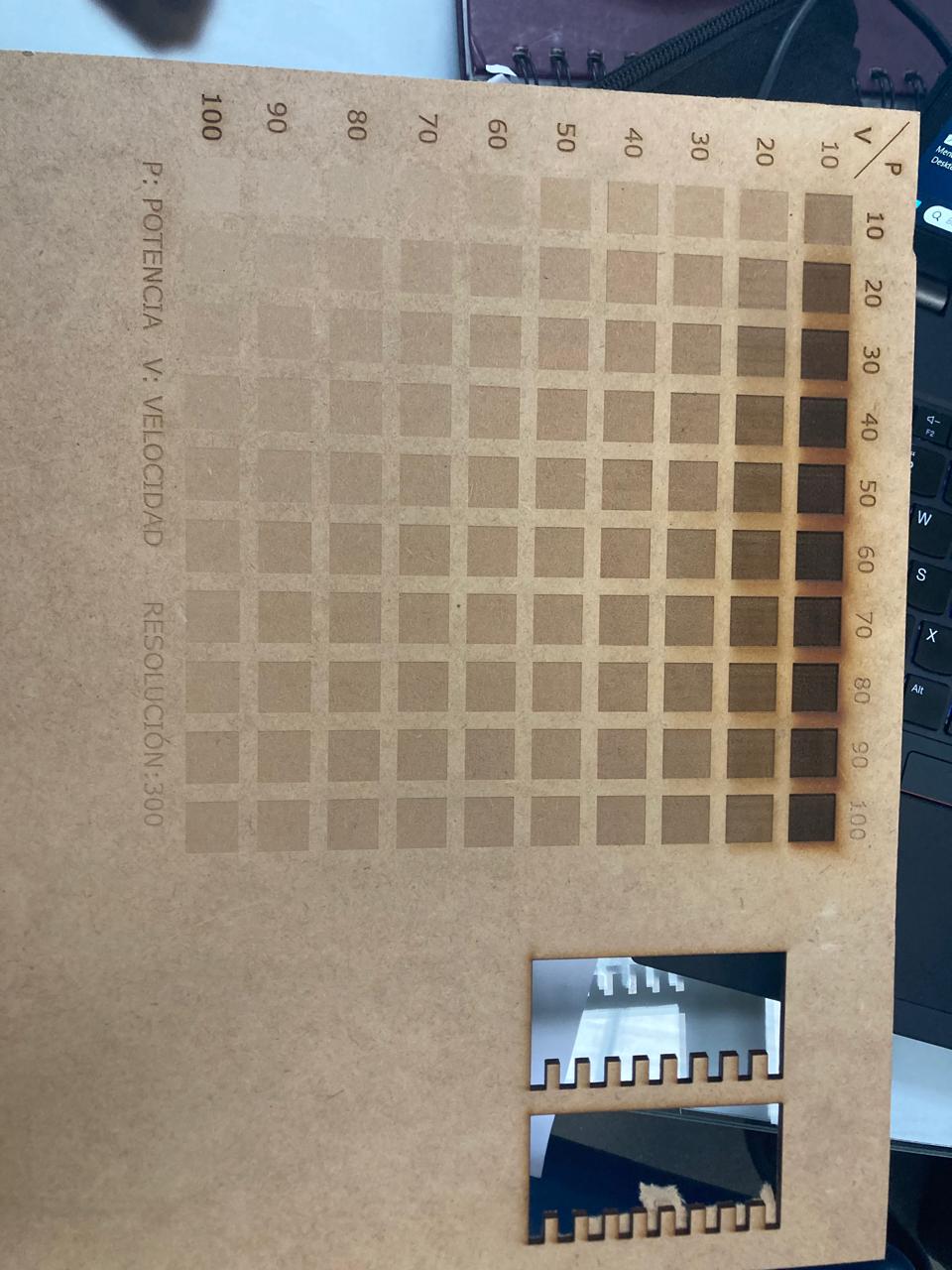
3.5 Laser Calibration Grid
- Displayed in the first image, the power vs. speed test grid is used to determine optimal settings for different materials.
- Power settings range from 10% to 100%
- Speed settings range from 10% to 100%
3.6 Safety Considerations
- Protective Gear: Safety glasses for reflective materials
- Machine Supervision: Never leave unattended
- Cleanliness: Regular maintenance to prevent overheating

4.1 Objective
This experiment aims to determine the optimal fit for interlocking laser-cut pieces by testing different slot widths and evaluating tolerances.
4.2 Process
- Material: Medium-density fiberboard (MDF) or plywood.
- Laser Cutter Used: Epilog FusionMaker.
- Slot Widths Tested: Ranging from 2.9 cm to 3.6 cm in 0.1 cm increments.
- Kerf Consideration: Adjustments were made to account for material removal by the laser.
- Laser Settings: Power, speed, and frequency optimized for minimal burning and clean cuts.
4.3 Observations
- Tighter Fits: Slots between 2.9 cm - 3.2 cm required force for assembly.
- Looser Fits: Slots between 3.4 cm - 3.6 cm allowed for easy but potentially unstable connections.
- Optimal Fit: Likely within the 3.2 cm - 3.3 cm range.
- Burn Marks: Indicating laser power may be slightly high or multiple passes were used.
4.4 Adjustments for Future Tests
- Refining kerf compensation based on precise measurements.
- Optimizing laser power and speed to reduce burns.
- Testing different materials like acrylic and plywood for comparison.
- Evaluating mechanical strength of each fit under load conditions.
4.5 Conclusion
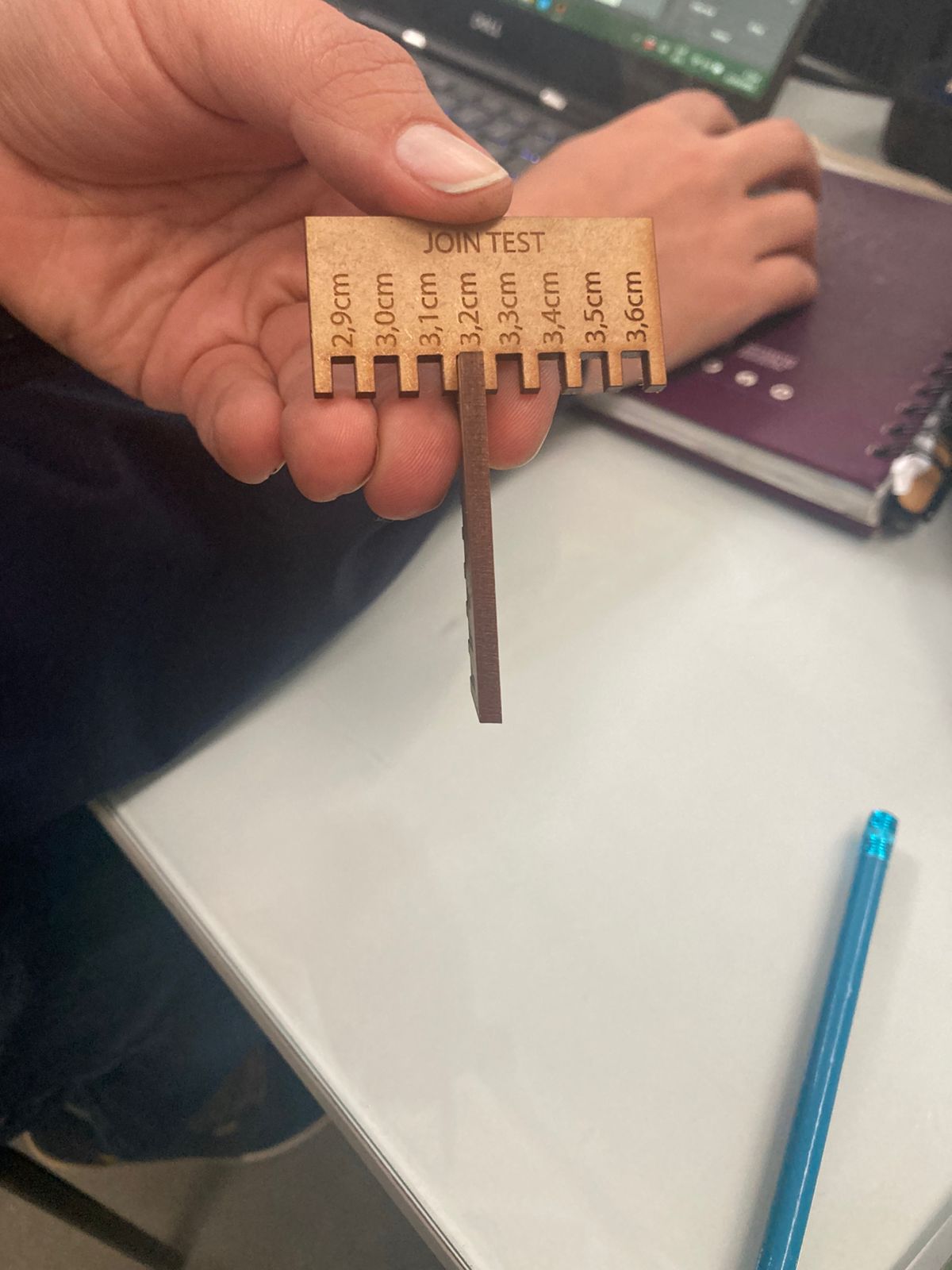
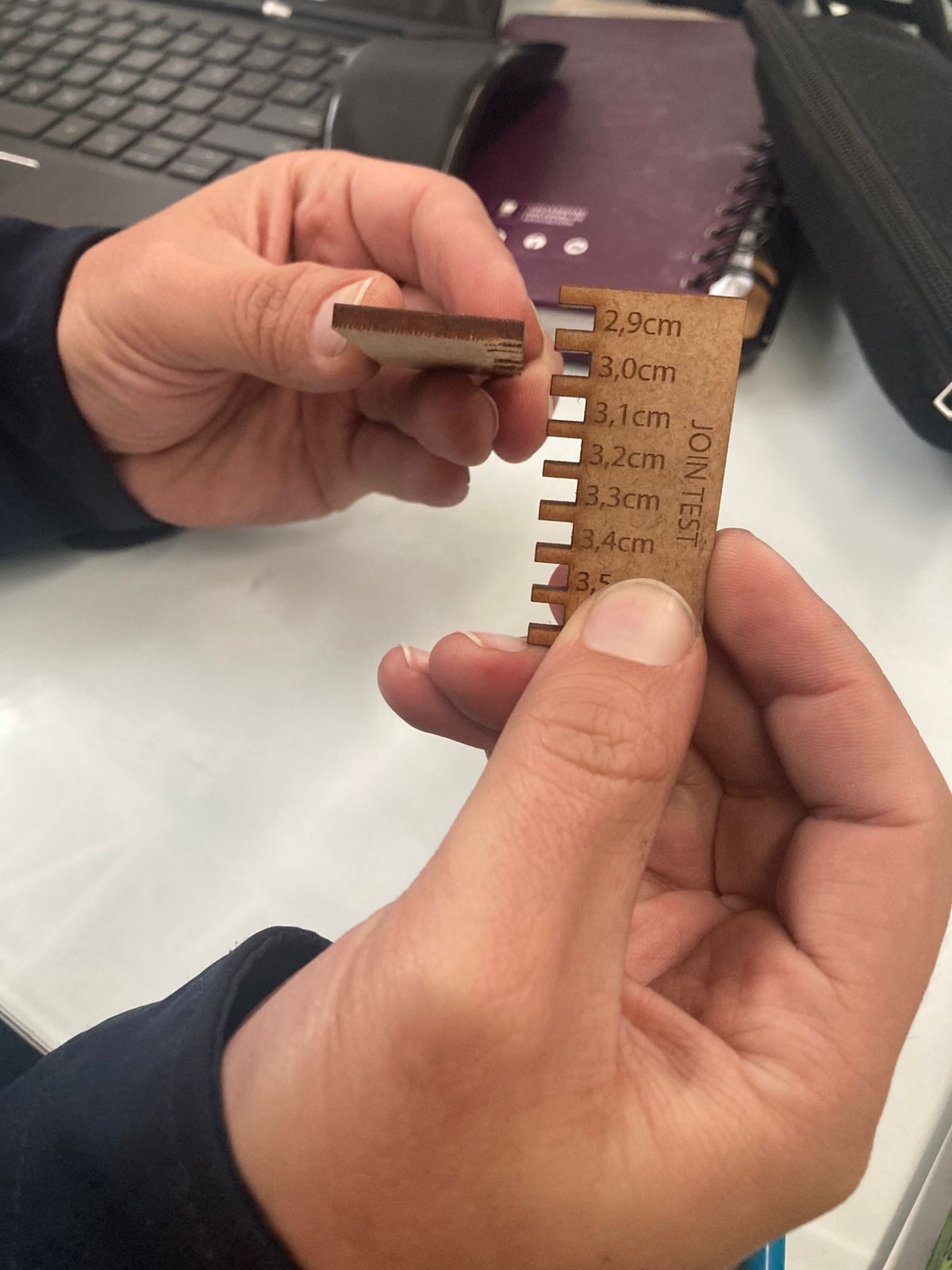



This test is essential for achieving precise fits in interlocking structures such as furniture, enclosures, and mechanical joints. Adjusting design files based on these results ensures accurate assembly and functional strength.
Individual Assignment

To Follow Vinyl Cutting
General Safety Guidelines
1. Prepare the file in vector format (Illustrator, Pdf, eps, Corel draw).
Illustrator is selected as the design software, the idea is to work on the FabLab logo, working with corporate colours and shapes that reflect the notion of a network.
Modeling in Illustrator
- Use the square tool to create the base shape.
- Join pieces using the union tool to form a single piece.
- Use copy and symmetry to create the final composition.

2. Set up the machine for cutting. It is decided to cut adhesive textile vinyl in such a way that

3. Start cutting
Transfer Vinyl Cutting on Fabric - Heat Transfer Vinyl
In principle, a heat press is used to apply heat and pressure to the vinyl, then the vinyl is placed with the hotmelt side facing the fabric. It is important to mention that the iron is adjusted according to the parameters of the vinyl. The plate is opened and then, the hot transfer film is removed. Textile cut vinyl is a thermo-adhesive plastic film that can be applied on cotton, cotton-polyester and polyester-acrylic fabrics.
1. Peeling
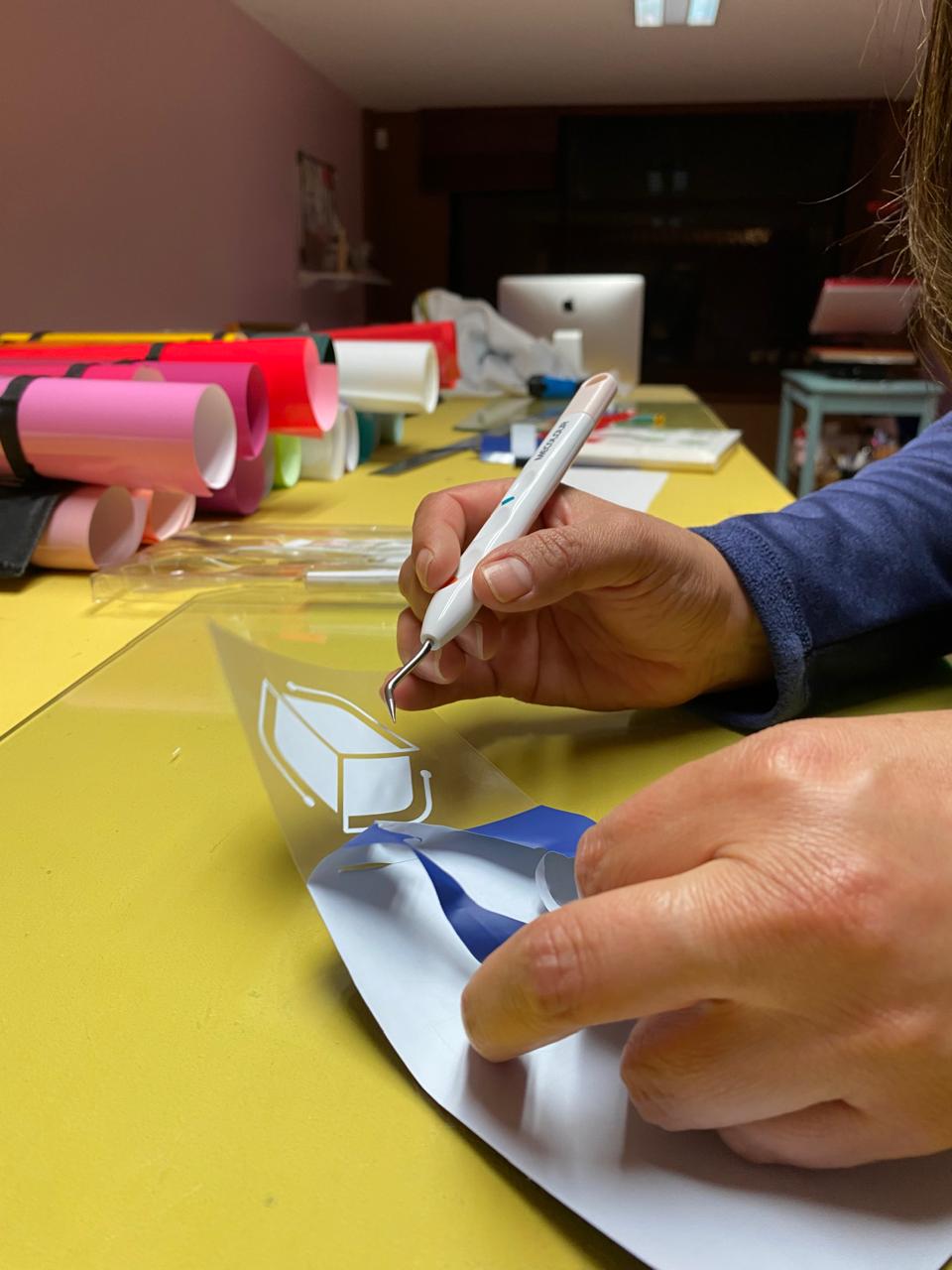
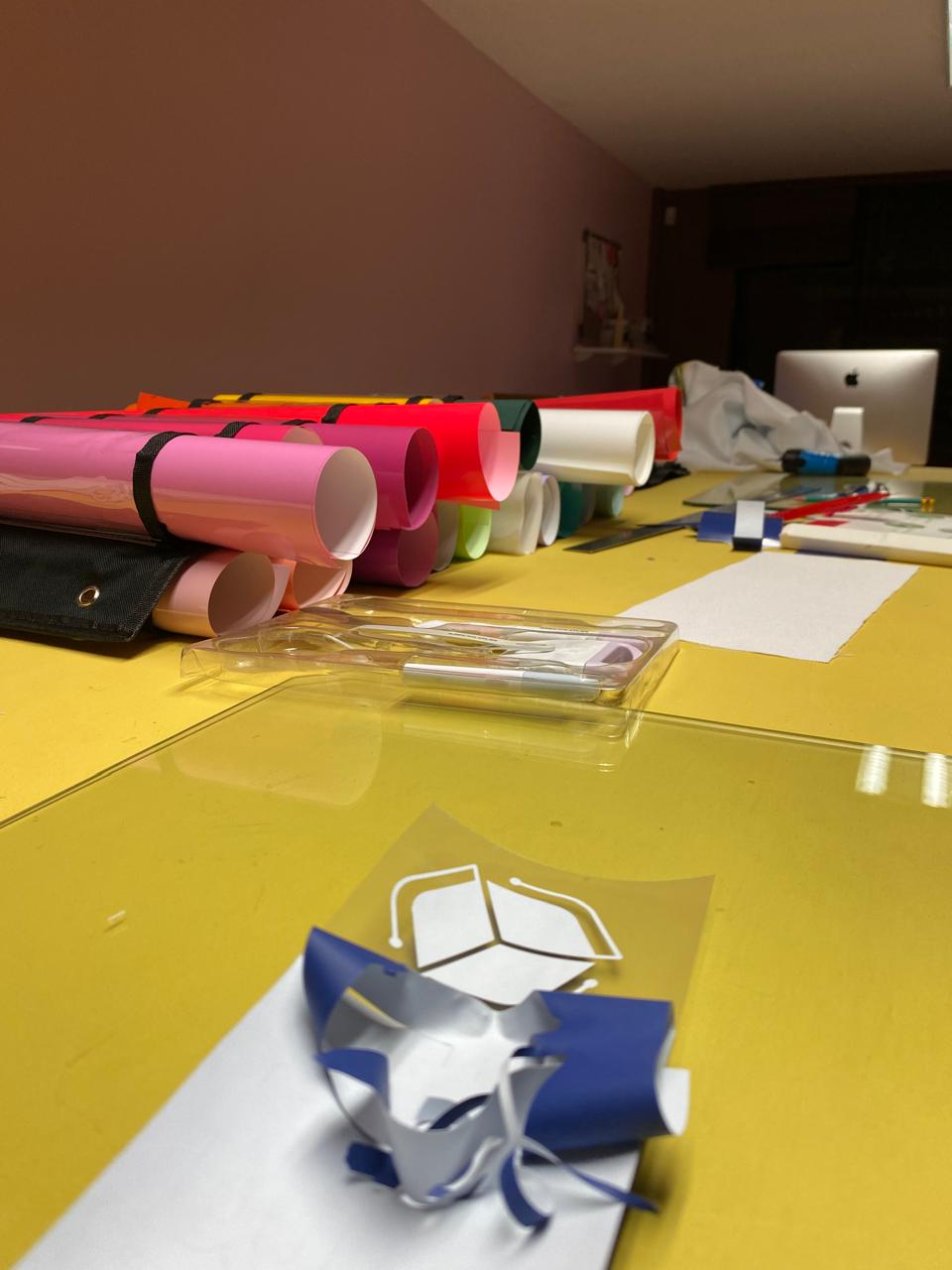


2. Stamping

3. Final product

Design and Laser Cutting Process
Open Illustrator.
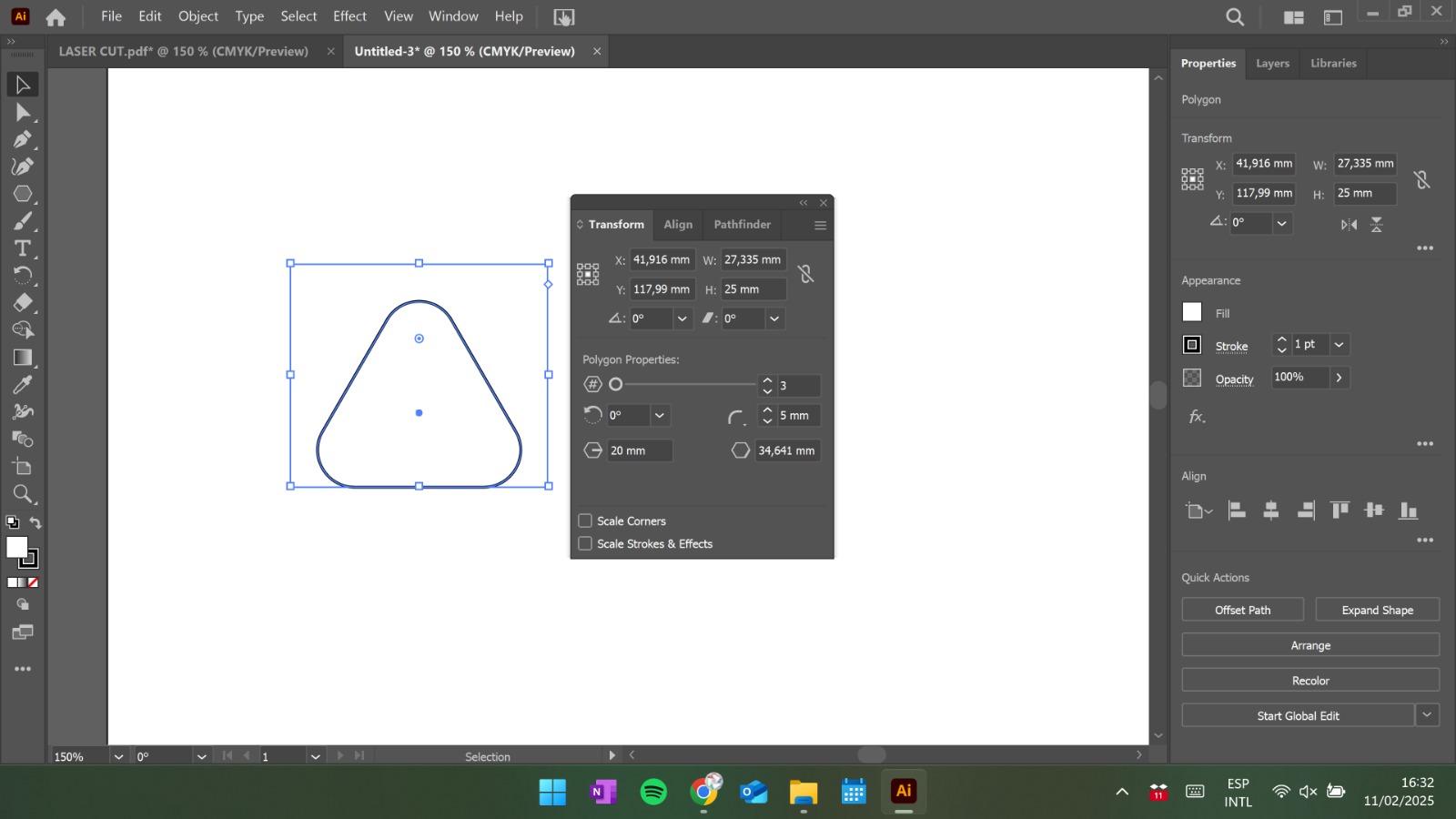
Draw the Piece: Create the 2D design with precise measurements.
Export to PDF: Generate a PDF file of the final design.
Send to Machine Software: Upload the PDF file to the cutting machine software.
Execute the Cut: Start the laser cutting process on the chosen material.
Kit: Assembled parts kit.
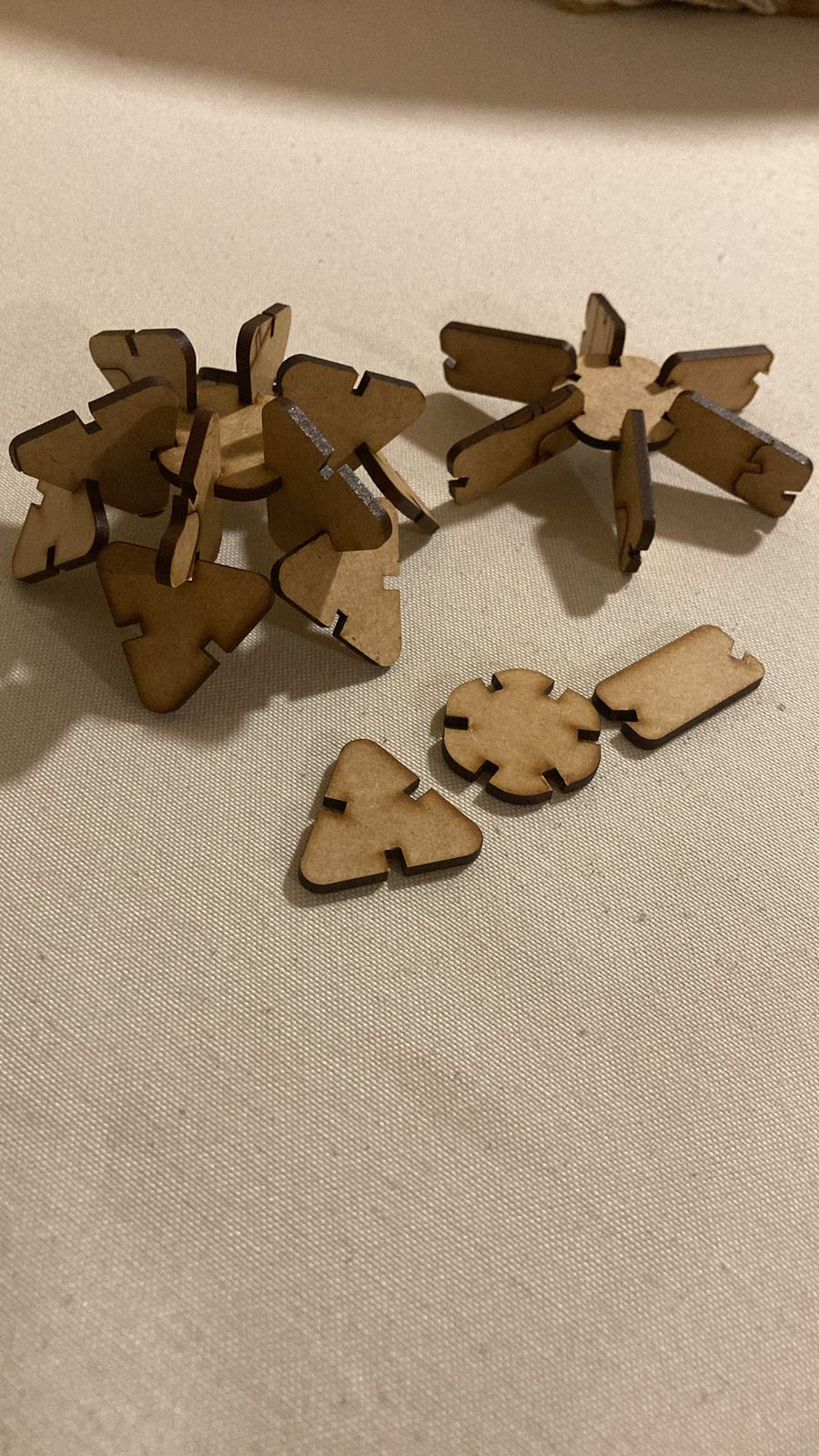

Conclusion
The practice of play is present in all cultures. It has evolved along with social construction in order to respond to the demands of the current context. In this sense, with the aim of designing the interaction between the elderly / play device techniques and digital fabrication tools are used to materialize the significant value of play focused on mitigating the cognitive impairment of the elderly through the stimulation of brain activity.